By alloying SG iron with Nickel, a stable austenitic nodular iron is produced, giving excellent resistance to growth and oxidation up to 925°C.
The main application for Ni-Resist is in Gas Turbine, Automotive Exhaust and Turbocharger Systems, where temperature fluctuates between 500 and 1050°C. Ni-Resist is suitable in these applications because its ductility, hot strength and low coefficient of thermal expansion, provide best resistance to such severe thermal shocks.
Physical properties depend on operating temperatures and the exact nickel composition of the SG iron alloy. However typical values for the austenitic Ni-Resist grade D5S are detailed below:
Castings P.L.C. Ni-Resist Ductile Iron conforms to:
ASTM A571:1984, grade D5S
EN-GJSA-XNiSiCr35-5-2
BS 3468:1986
DIN 1694: GGG-NiSiCr35.5.2
| Typical Chemical Composition | |
|---|---|
| C | 2.0% max |
| Si | 4.0 - 6.0% |
| Mn | 0.5 - 1.5% |
| Ni | 34.0 - 36.0% |
| Cr | 1.5 - 2.5% |
| P | 0.08% max |
| Cu | 0.50% max |
| Mechanical Properties | |
|---|---|
| Tensile Strength (Rm) | 380 - 500 N/mm2 |
| Proof Stress (Rp0.2) | 210 - 270 N/mm2 |
| Elongation (A) | 10 - 20 % |
| Modulus of Elasticity (E) | 130 - 150 kN/mm2 |
| Brinell Hardness | 130 - 170 HB |
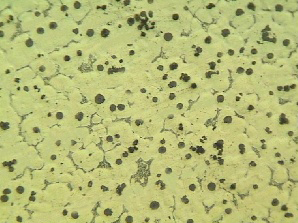
Ni Resist Microstructure
Guideline figures for maximum Manifold temperatures
| Max. Manifold Temp °C | Max. Exhaust Gas Temp °C | |
|---|---|---|
| SG400/15 | 700 | 770 |
| SiMo 0.5% | 750 | 820 |
| SiMo 1% | 780 | 820 |
| SiMo Ni | 795 | 835 |
| Ni Resist D5S | 870 | 950 |
